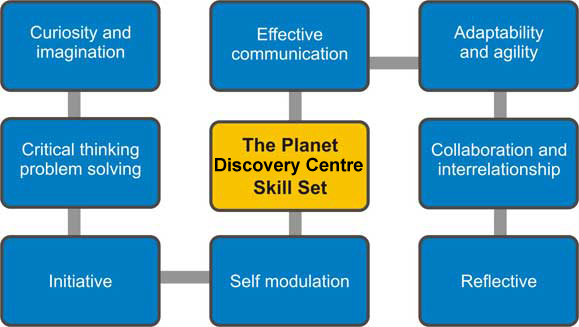
 Skill Set
Skill Set
8 areas of development and skills
The alignment of development initiates the child as a “lifelong learner” in a natural setting.
The impact of skill, behaviour or growth mindset has an impact on academic achievement.
A measureable skill is that differentiates between personality, character traits and learner attributes.
Curiosity and imagination
The desire to engage and understand the world, interest in a wide variety of things and preference for a complete understanding of a complex topic or problem.
Goff, M., & Ackerman, P., (1992).
Ability to think what “it”could be in terms of size, shape, colour
Effective communication
The ability to convey or share ideas and feelings effectively .Reading ,writing , speaking, listening , and visual presentation makes language the core for thinking and communicating effectively.
Ability to make oneself understood orally and /or using body language
Adaptability and agility
Positive adaptation during or following exposure to adversities that have the potential to harm development: (a) developing well in the context of high cumulative risk for developmental problems (beating the odds, better than predicted development), (b) functioning well under currently-adverse conditions (stress-resistance, coping) and (c) recovery to normal functioning after catastrophic adversity (bouncing back, self-righting) or severe deprivation (normalization). Wherein students ascribe to the belief: my ability and competence grow with my effort. A deep and enduring emotional bond that connects one person to another across time and space.
ability to maintain calm and remain productive in different situations.
Farrington, et al., (2012).
Critical thinking and problem solving
ability to be logical for solving any problem
Collaboration and interrelationship
The ability to take the perspective of, and empathize with, others from diverse backgrounds and cultures, to understand social and ethical norms for behavior, and to recognize family, centre and community resources and supports.
ability to appreciate that working with others is advantageous to the self
Payton, J. et al., (2008).
initiative Self-Direction
A process in which learners take the initiative in planning, implementing and evaluating their own learning needs and outcomes, with or without the help of others The initiative to provide them the learner autonomy.
ability to complete a task on his /her own
Knowles, M.S., (1975).
Self modulation
The ability to take the perspective of, and empathize with, others from diverse backgrounds and cultures, to understand social and ethical norms for behavior, and to recognize family, centre and community resources and supports.
Ainsworth, M.D.S., (1973).
ability to appreciate that each person is unique in terms of his /her behaviour and the need to change oneself to suit the specific situation –to get the maximum benefit
Reflective
The ability to accurately recognize one’s emotions and thoughts and their influence on behavior. This includes accurately assessing one’s strengths and limitations and possessing a well-grounded sense of confidence and optimism.
ability to spend time on own to think what was done ,why it was done in that manner, what could have been done in that situation and how it should be done in future
Payton, J. et al., (2008).

